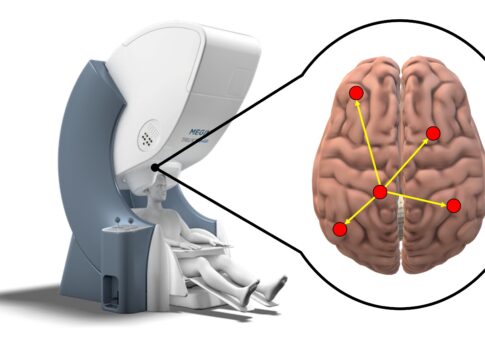
Abstract Intrinsic brain dynamics co-fluctuate between distant regions in an organized manner during rest, establishing large-scale functional networks. We investigate these brain dynamics on a millisecond time scale by focusing on electroencephalographic (EEG) source analyses. While synchrony is thought of as a neuronal mechanism grouping distant neuronal populations into assemblies, the relevance of simultaneous zero-lag synchronization between brain areas in humans remains largely unexplored. This negligence is because of the confound of volume conduction, leading inherently to temporal dependencies of source estimates derived from scalp EEG [and magnetoencephalography (MEG)], referred to as spatial leakage. Here, we focus on the analyses of simultaneous, i.e., quasi zero-lag related, synchronization that cannot be explained by spatial leakage phenomenon. In eighteen subjects during rest with eyes closed, we provide evidence that first, simultaneous synchronization is present between distant brain areas and second, that this long-range synchronization is occurring in brief epochs, i.e., 54–80 ms. Simultaneous synchronization might signify the functional convergence of remote neuronal populations. Given the simultaneity of distant regions, these synchronization patterns might relate to the representation and maintenance, rather than processing of information. This long-range synchronization is briefly stable, not persistently, indicating flexible spatial reconfiguration pertaining to the establishment of particular, re-occurring states. Taken together, we suggest that the balance between temporal stability and spatial flexibility of long-range, simultaneous synchronization patterns is characteristic of the dynamic coordination of large-scale functional brain networks. As such, quasi zero-phase related EEG source fluctuations are physiologically meaningful if spatial leakage is considered appropriately.
Publication scientifique
Synchronous Brain Dynamics Establish Brief States of Communality in Distant Neuronal Populations
Autres publications de la plateforme
Causal disconnectomics of motion perception networks: insights from transcranial magnetic stimulation‐induced...
Boosting hemianopia recovery: the power of interareal cross-frequency brain stimulation
Return of the GEDAI: Unsupervised EEG Denoising based on Leadfield Filtering
Multivariate deep phenotyping reveals behavioral correlates of non-restorative sleep in 22q11.2...
EEG microstate D as psychosis-specific correlate in adolescents and young adults...
EEG correlates of egocentric and altercentric biases in forensic cases with...
Journal de publication
Auteurs:
Date de publication:
Plateforme:
Études récentes de la plateforme

Améliorer la récupération motrice du bras après un AVC

Restaurer le mouvement après une paralysie