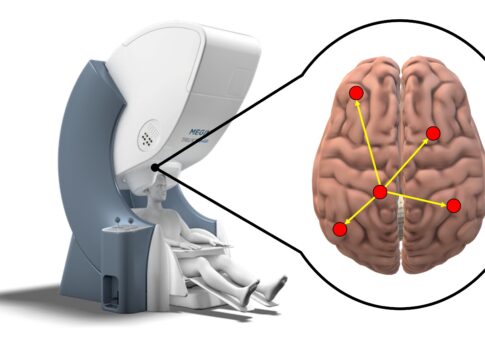
Electroencephalography (EEG) based brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) offer a promising way for individuals with motor impairments to control prosthetic or rehabilitation devices. Accurately decoding movement intention (MI) is crucial for translating subjects’ motor execution plans into action. Common challenges in EEG-based BCIs include performance discrepancies, often requiring frequent recalibration of decoding algorithms. The objective of this study was enhancing BCI decoding performance of upper-limb MI identification by exploiting both machine and subjects’ learning and maintaining stable decoding algorithms. Significant performance improvements were observed across most subjects from the first to the last session of the experiment. Some subjects also demonstrated stable performance without requiring any model recalibration between sessions. All subjects achieved high efficacy in online decoding of movement intention, as reflected in improvement of the F1 score from 0.58pm 0.26 in the first session, to 0.84pm 0.13 in the final session. We emphasize the critical importance of allowing users sufficient time to improve their performance in BCIs for upper-limb MI decoding. Unlike existing studies, we specifically evaluate the effect of stable decoding strategies in online and longitudinal BCI sessions, which are key to achieving more reliable and effective BCIs.
Publication scientifique
The Effect of User Learning for Online EEG Decoding of Upper-Limb Movement Intention
Autres publications de la plateforme
Causal disconnectomics of motion perception networks: insights from transcranial magnetic stimulation‐induced...
Boosting hemianopia recovery: the power of interareal cross-frequency brain stimulation
Return of the GEDAI: Unsupervised EEG Denoising based on Leadfield Filtering
Multivariate deep phenotyping reveals behavioral correlates of non-restorative sleep in 22q11.2...
EEG microstate D as psychosis-specific correlate in adolescents and young adults...
EEG correlates of egocentric and altercentric biases in forensic cases with...
Journal de publication
Auteurs:
Date de publication:
Plateforme:
Études récentes de la plateforme

Restaurer le mouvement après une paralysie
Comment les souvenirs évoluent-ils avec le temps ?