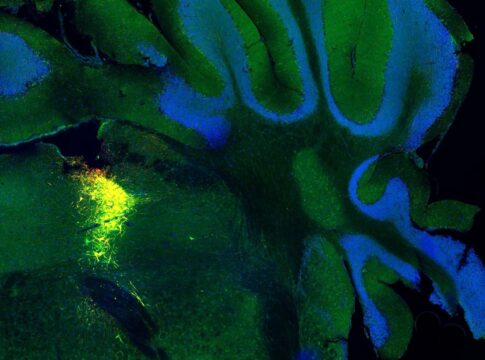
Intrafascicular stimulation evokes precise and functional hand movements in monkeys, suggesting clinical opportunities for people with hand paralysis. , It is TIME to move your hand Upper limb paralysis can develop after spinal cord injury or stroke. Electrical stimulation has been used to partially restore hand movements; however, current approaches using surface or intramuscular stimulation require challenging surgeries and/or have limited efficacy and are associated with important adverse effects. Here, Badi et al. developed an intraneural transverse intrafascicular multichannel electrode (TIME) system, composed of two electrodes for stimulation of the median and radial nerve, that was able to restore hand movements in primates. In a proof-of-principle experiment, one paralyzed monkey was able to perform hand movements using a brain-controlled TIME. Intrafascicular stimulation might be used for generating and allowing fine hand movements in paralyzed patients. , Restoring dexterous hand control is critical for people with paralysis. Approaches based on surface or intramuscular stimulation provide limited finger control, generate insufficient force to recover functional movements, and require numerous electrodes. Here, we show that intrafascicular peripheral electrodes could produce functional grasps and sustained forces in three monkeys. We designed an intrafascicular implantable electrode targeting the motor fibers of the median and radial nerves. Our interface selectively and reliably activated extrinsic and intrinsic hand muscles, generating multiple functional grips, hand opening, and sustained contraction forces for up to 2 months. We extended those results to a behaving monkey with transient hand paralysis and used intracortical signals to control simple stimulation protocols that enabled this animal to perform a functional grasping task. Our findings show that just two intrafascicular electrodes can generate a rich portfolio of dexterous and functional hand movements with important implications for clinical applicability.
Publication scientifique
Intrafascicular peripheral nerve stimulation produces fine functional hand movements in primates
Autres publications de la plateforme
Hypothalamic deep brain stimulation augments walking after spinal cord injury
A neuronal architecture underlying autonomic dysreflexia
Dual lineage origins contribute to neocortical astrocyte diversity
Urolithin A provides cardioprotection and mitochondrial quality enhancement preclinically and improves...
Regional differences in progenitor metabolism shape brain growth during development
Journal de publication
Auteurs:
Date de publication:
Plateforme:
Études récentes de la plateforme

Restaurer le mouvement après une paralysie

Reconnecter le cerveau social